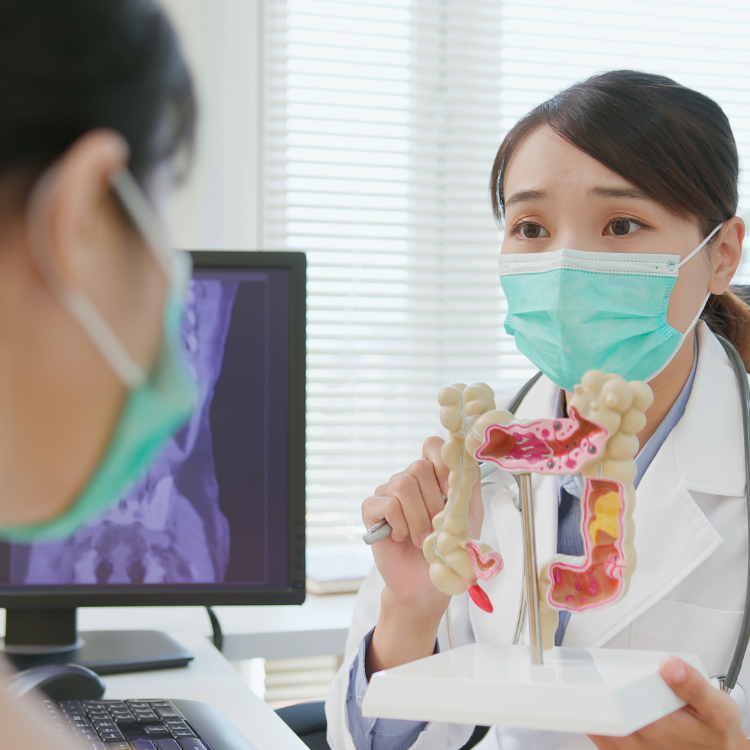
Colorectal cancer surgery is a key component of the management of colorectal cancer, which is the third most common cancer globally. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous tissue and surrounding lymph nodes while preserving bowel function and minimizing the risk of complications. Laparoscopic surgery, which involves the use of minimally invasive techniques and specialized instruments, has become the preferred approach for many colorectal surgeries, as it offers many advantages over traditional open surgery, such as smaller incisions, reduced pain and scarring, and faster recovery times.
Colorectal cancer screening is an essential tool in the early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer. Various screening methods are available, including colonoscopy, fecal occult blood testing, and stool DNA testing. The American Cancer Society recommends that individuals at average risk of colorectal cancer begin screening at age 45, while those at higher risk may need to start earlier and undergo more frequent screening.
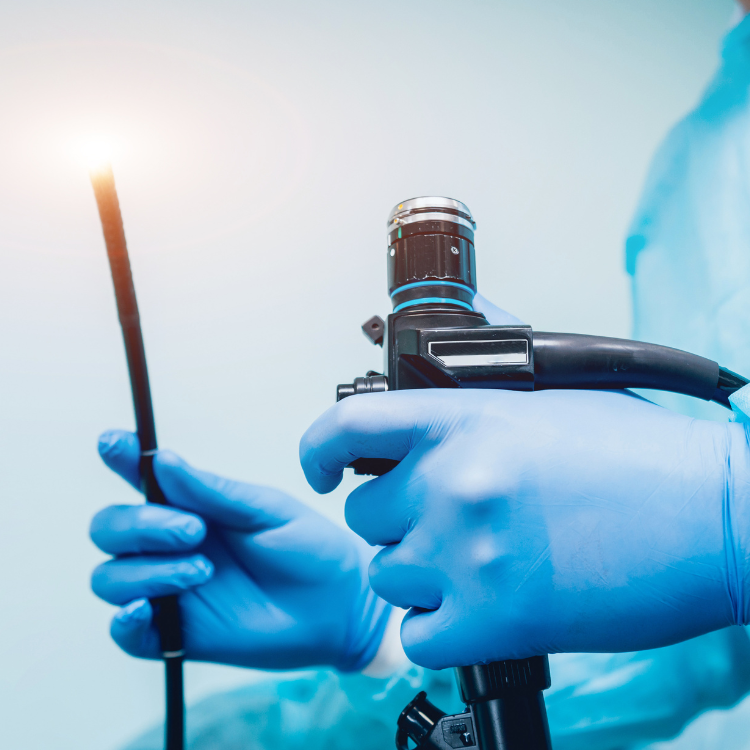

Gallstone disease is a common condition that occurs when solid particles, called gallstones, form in the gallbladder. These stones can cause inflammation, pain, and other complications. Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is usually the preferred option for the treatment of gall stone disease.

Cytoreductive surgery with HIPEC is a specialized surgical technique used in the treatment of advanced abdominal cancers, such as pseudomyxoma peritonei and peritoneal mesothelioma. It is also done for other cancers with peritoneal metastasis. The procedure involves the removal of cancerous tissue and the administration of heated chemotherapy directly into the abdominal cavity, which can improve survival rates and quality of life for some patients.